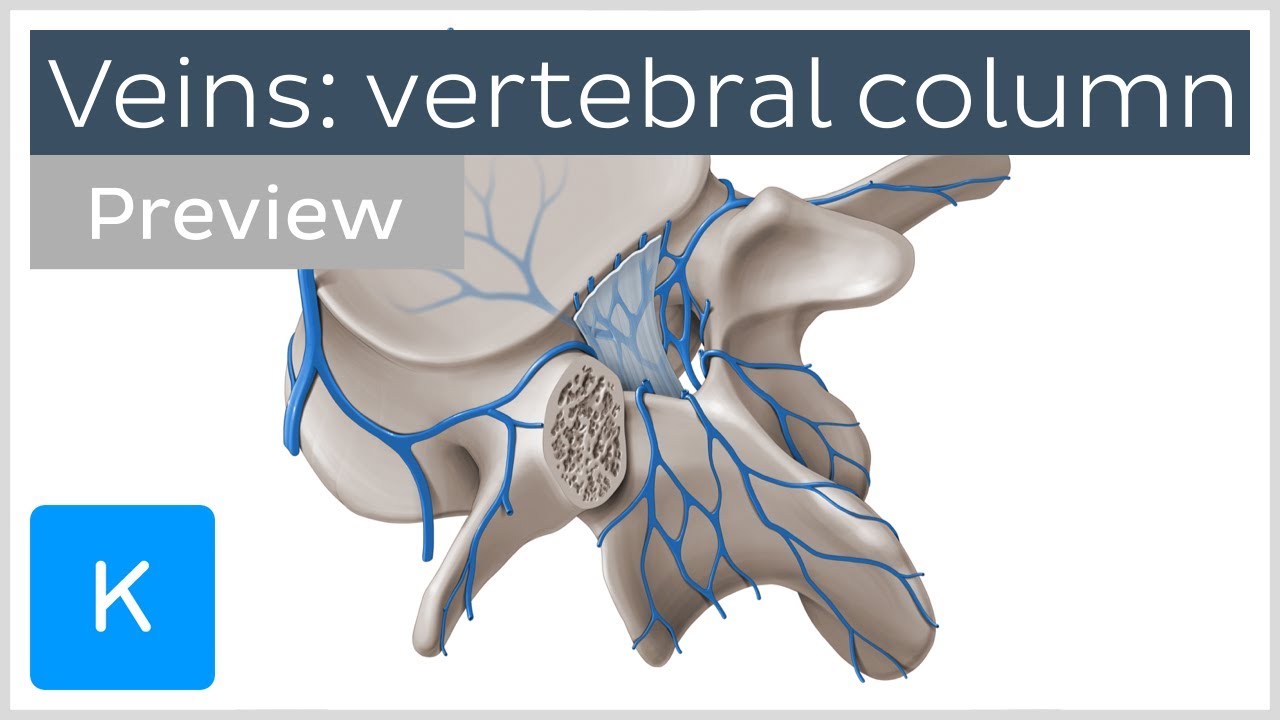
Veins of the Vertebral Column (preview) Human Anatomy Kenhub YouTube
Starting at vertebral levels T12-L2, the azygos vein travels posterior to the right root of the lung (T5-T6) and arches superiorly over the root of the lung, emptying into the SVC. Sometimes, the azygos vein may travel higher to drain into the brachiocephalic or right subclavian vein.

The Cervical Spinal Cord and Origin of the Anterior Spinal Artery. The... Download Scientific
In the neck, the plexus drains to the vertebral vein and deep cervical veins [ 1 ]. In summary, the venous drainage of the spinal cord consists of internal cord veins, longitudinal cord veins, and radicular veins. Internal cord vein anatomy differs depending on the spinal segment; however, most drain centrifugally (with a radiating pattern.
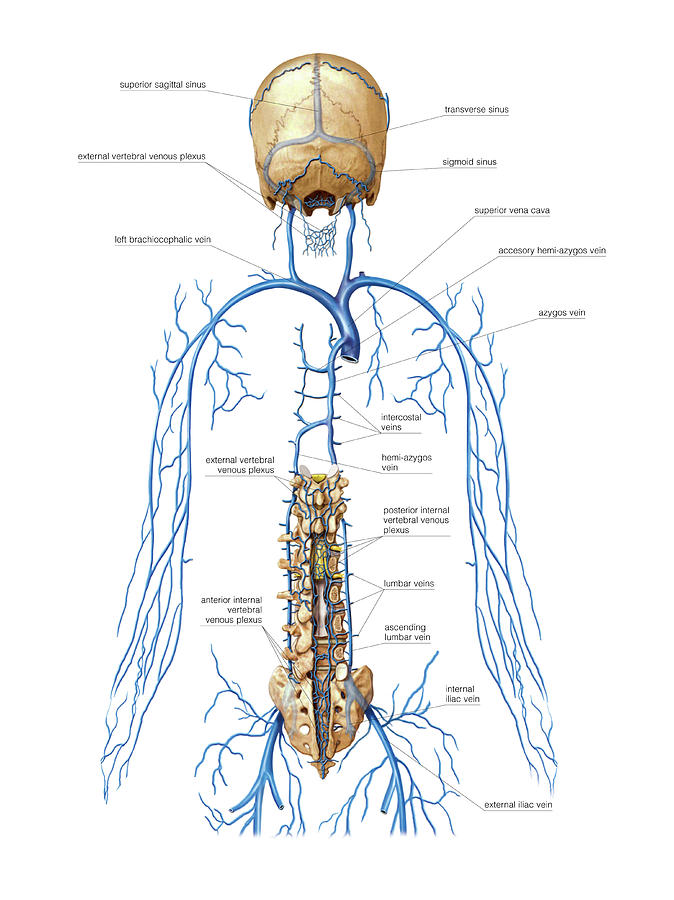
Venous System Of Vertebral Venous Plexus Photograph by Asklepios Medical Atlas Pixels
The vertebral column is drained by plexuses (networks) of veins. These venous plexuses are formed by spinal veins along the vertebral column, both inside and outside the vertebral canal. The plexuses include: Internal vertebral venous plexus (or the epidural venous plexus) External vertebral venous plexuses Anterior internal vertebral venous plexus

Vertebral Artery Ultrasound Radiologic Clinics
Vena vertebralis anterior Quick Facts Origin Course Tributaries Structures Drained Quick Facts Origin: Around the transverse processes of the upper cervical vertebrae. Course: Descends in the neck to drain into the vertebral vein. Tributaries: Anterior external vertebral venous plexus. Drainage: Vertebral column. Complete Anatomy

The vertebral venous plexus comprises an interconnected and richly... Download Scientific Diagram
The vertebral vein is a paired blood vessel that is found on either side of the neck. As a single vessel, it is formed at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra (C6). Its initial part is a venous plexus that goes through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae. Check it out

Vascular anatomy
Anatomy of Spinal Venous Drainage for the Neurointerventionalist: From Puncture Site to Intervertebral Foramen N. Borg, J. Cutsforth-Gregory, S. Oushy, T. Huynh, L.E. Savastano, H.J. Cloft, G. Lanzino and W. Brinjikji American Journal of Neuroradiology January 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A7409 Article Figures & Data Info & Metrics

Vertebral Artery Art Print by Asklepios Medical Atlas
The blood supply to the vertebral canal is critical especially from the context of surgical and clinical considerations. The spinal cord located within the vertebral canal allows for a neuronal connection between the brain and the rest of the body and thus the blood supply to this structure is of vital importance. In this review, we go over the blood supply as well as additional information.
Vertebral Artery Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The vertebral vein is a paired vessel found in the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae on either side of the neck. It arises at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra from a venous plexus that surrounds the vertebral artery and travels as far as the brachiocephalic veins.

Ascending and Descending Thoracic Vertebral Arteries AJNR Blog
Spinal Vascular Malformations. This section is intended as an introduction to the (daunting) topic of spinal vascular anatomy. As interventionalists, we usually deal with two broad types of spinal issues — various vascular malformations and tumors. In the former group, we are mainly concerned with fistulas (dural, pial, cord) — not because.

Vertebral Artery Segments, Stenosis and Artery Dissection Symptoms
Structure and Function The spinal venous system consists of the intrinsic, extrinsic, and extradural systems. During IVC occlusion, the spinal venous system can serve as a collateral drainage system due to its connection with both pelvic and cranial veins. [1]

Left and Right Subclavian Artery Function, Branches, Stenosis
This article reviews the arterial and venous anatomy of the spine and spinal cord. Special emphasis is placed on vessels critical to the conduct and interpretation of spinal angiography, notably the intersegmental artery and its cranial and caudal derivatives: the vertebral, supreme intercostal, and sacral arteries.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/vertebral-artery/Pr3DUiOydFe8hJ3WXcIg_qZw8tXTIX5JHJ79oMmfKA_Vertebral_artery.png)
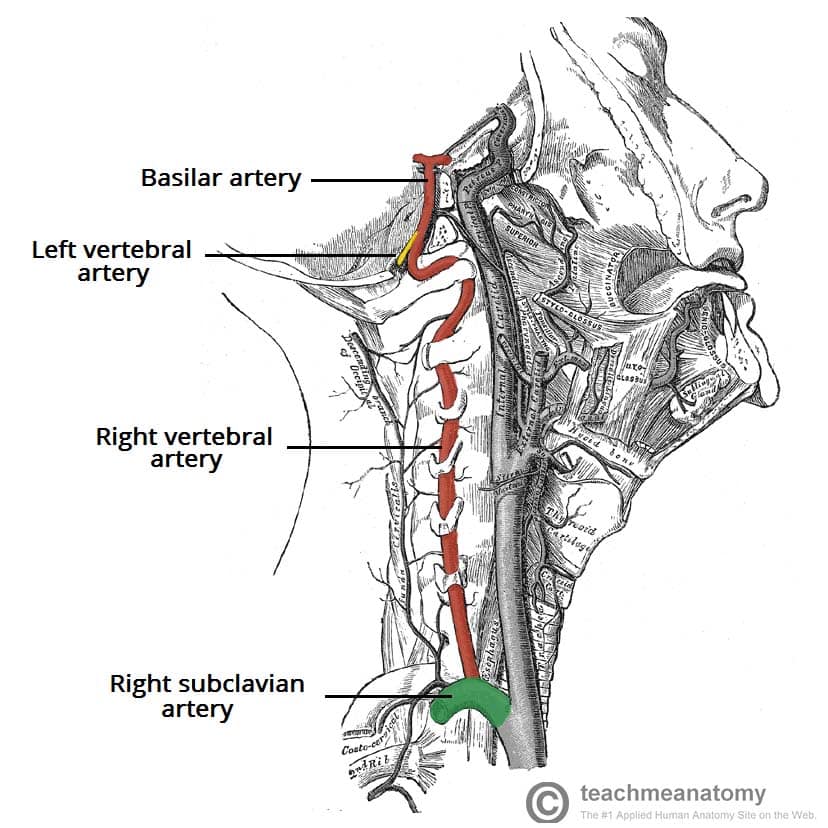
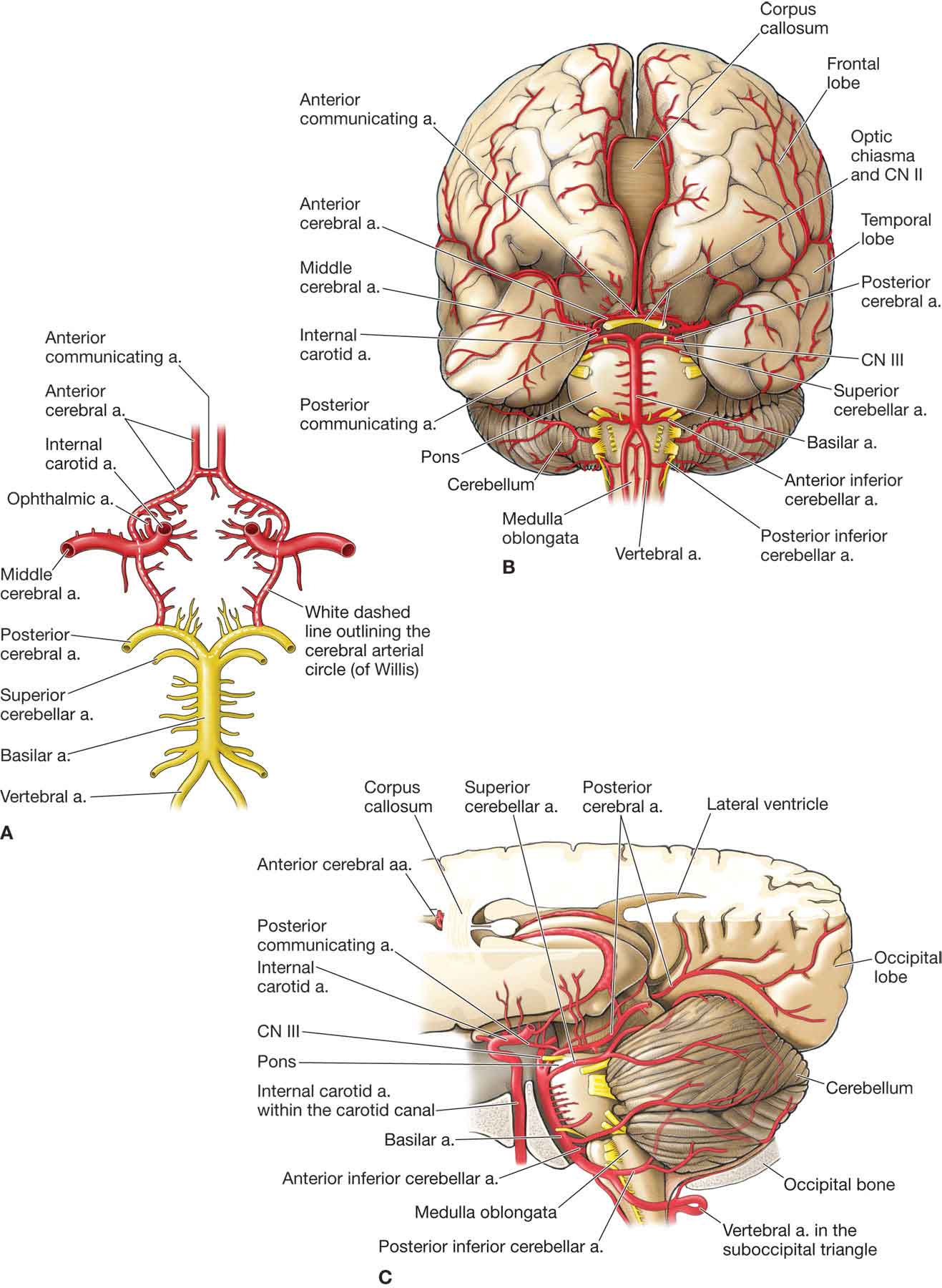
Vertebral artery Course, Segments, Branches Kenhub
Vertebral Arteries (VA): 4 Segments V1 - Extraosseous segment Origin from each subclavian artery, coursing superiorly to enter the C6 transverse foramen (80-90%) Variations Origin of the left vertebral artery from the aortic arch between the left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery has been described in 2-6% of cases
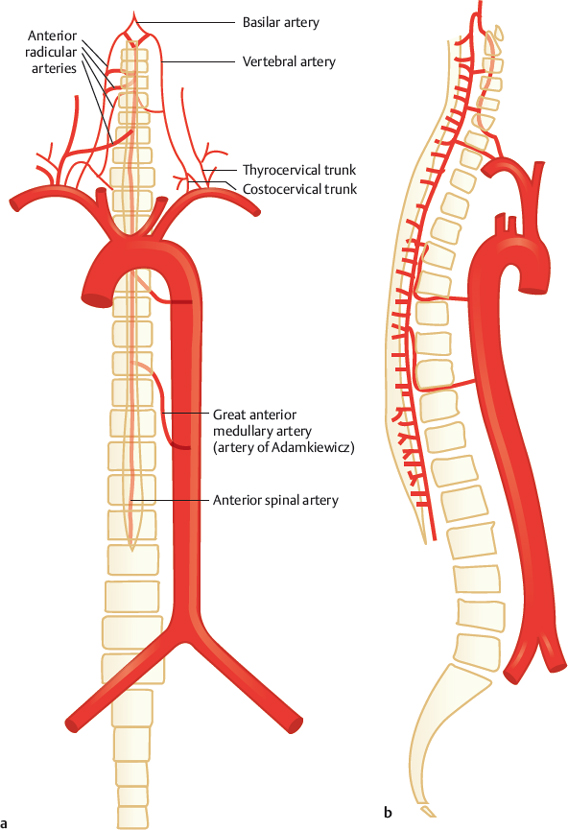
Arteries of the Spinal Cord Radiology Key
The lumbar veins are four pairs of blood vessels that drain the lumbar segments of the spinal cord, posterolateral abdominal wall and lumbar structures of the back. They usually empty into the inferior vena cava, but they can also drain into the ascending lumbar, azygos, renal or other lumbar veins.

Vertebral Artery Segments, Stenosis and Artery Dissection Symptoms
a -centripetal network of veins, predominantly draining the gray matter into: b - central (sulcal) veins of the intrinsic system; c - peripheral (radial, a.k.a. marginal) centrifugal veins of the intrinsic system; d - venous anastomosis between the centripetal and centrifugal systems; e - anterior (ventral) median vein; f - posterior (dorsal) me.
Vertebral Artery Musculoskeletal Key
The vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs. It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx. The spinal cord runs through its center.

Veins of Vertebral Column Vertebral Veins Anatomy Superior bulb of right internal jugular vein
The vertebral vein (Latin: vena vertebralis) is a venous blood vessel that is formed by numerous small tributaries arising from the internal vertebral plexuses. The vertebral vein collects venous blood mainly from the upper deep muscles of the back. Vertebral vein by Anatomy.app